Circadian System Explained - Learning Objectives
You can participate in research -'myCircadianClock' app - click here.Circadian Code BookDr. Satchin Panda is a leading expert in the field of circadian rhythm research. He is a Professor at the Salk Institute and a, founding executive member of the Center for Circadian Biology at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Panda is a Pew Scholar and a recipient of the The Julie Martin Mid-Career Award in Aging Research.
Beginning with an in-depth explanation of the circadian clock—why it’s important, how it works, and how to know it isn’t working--The Circadian Codeoutlines lifestyle changes to make to get back on track. It’s a concrete plan to enhance weight loss, improve sleep, optimize exercise, and manage technology so that it doesn’t interfere with your body’s natural rhythm. Dr. Panda’s life changing methods show you how to prevent and reverse ailments like diabetes, cancer, and dementia, as well as microbiome conditions like acid reflux, heartburn, and irritable bowel disease. Circadian System
Our ancestors evolved under the natural cycles of day-light and dark -night. Light is energy that influences mind and body - many chemicals in our bodies are controlled by light.
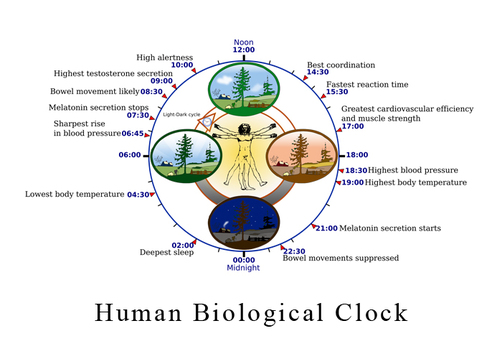
Premature babies thrive under simulated sunrise to sunset - where the light changes color throughout the day, and they have a dark night sleep. Studies have shown them growing at a rate 50% faster than those under constant bright illumination. [1] This makes sense, since we grow and heal while we sleep, naturally in the dark. Melatonin is produced at night to direct our bodies to sleep. Exposure to blue tinted light can delay sleep for as much as two hours. This Biological Clock diagram represents the natural circadian rhythm of a human day and night.
"A circadian rhythm /sɜːrˈkeɪdiən/ is any biological process that displays an endogenous, entrainable oscillation of about 24 hours. These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in plants, animals, fungi, and cyanobacteria." [1]
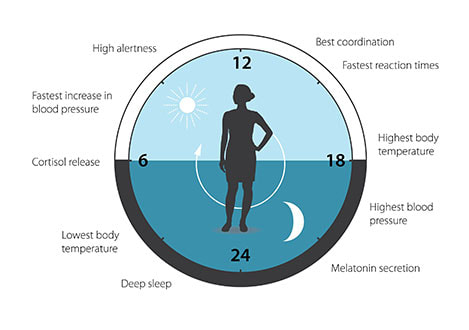
2017 Nobel Prize for Circadian Rhythm ResearchThe circadian clock anticipates and adapts our physiology to the different phases of the day. Our biological clock helps to regulate sleep patterns, feeding behavior, hormone release, blood pressure, and body temperature. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017, for their discoveries of molecular mechanisms controlling the circadian rhythm Jeffrey C. Hall, Michael Rosbash, Michael W. Young [3] |
Circadian BrainBrain Signals
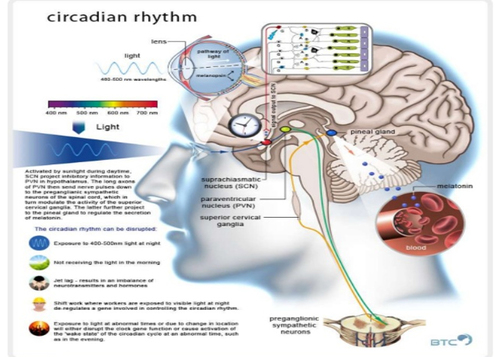
The controller of our Circadian System producing Melatonin is the Pineal Gland, this part of the Endocrine System, sometimes referred to as the 'third eye' is located deep inside our brain, directly above the optic chiasm. . It receives signals though our eyes, collecting information about light intensity and color via the optic nerves. "Suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), located in the hypothalamus above the optic chiasm."
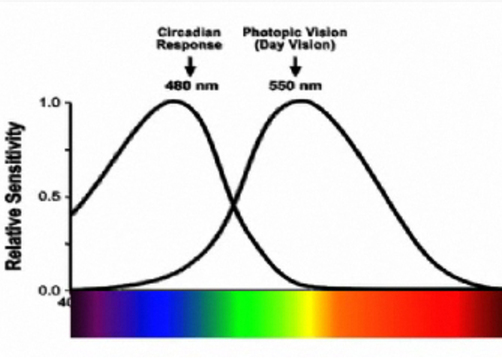
Hormones - Melatonin and Serotonin, are created in our bodies to signal us to sleep and wake. Cyto-architecture is a biology term used to describe the study of the arrangement of cells and how this affects the performance of each organ. Often referred to as study of the brain structure, 'cyto' means 'cells' and 'architecture' originates from Greek arkhitekton 'master builder.' Studying the architecture of the brain, is analogous to the study of buildings, their manner of construction and the arrangement of their parts. As recently as 2002 scientists discovered photoreceptors called ganglion cells (RGC) in our eye's retina that respond to light and send signals to our circadian system. Scientists continue to search for understanding of the brain circuits, receptors, and their functions. [4] Circadian Response Curve
|
Related Topics
|