Learning Objectives
Why is the sky blue?Combine all colors in light and you get white or combine any three colors equidistant on the color wheel to produce white light, usually red + green + blue producing magenta, turquoise, and yellow shadows.
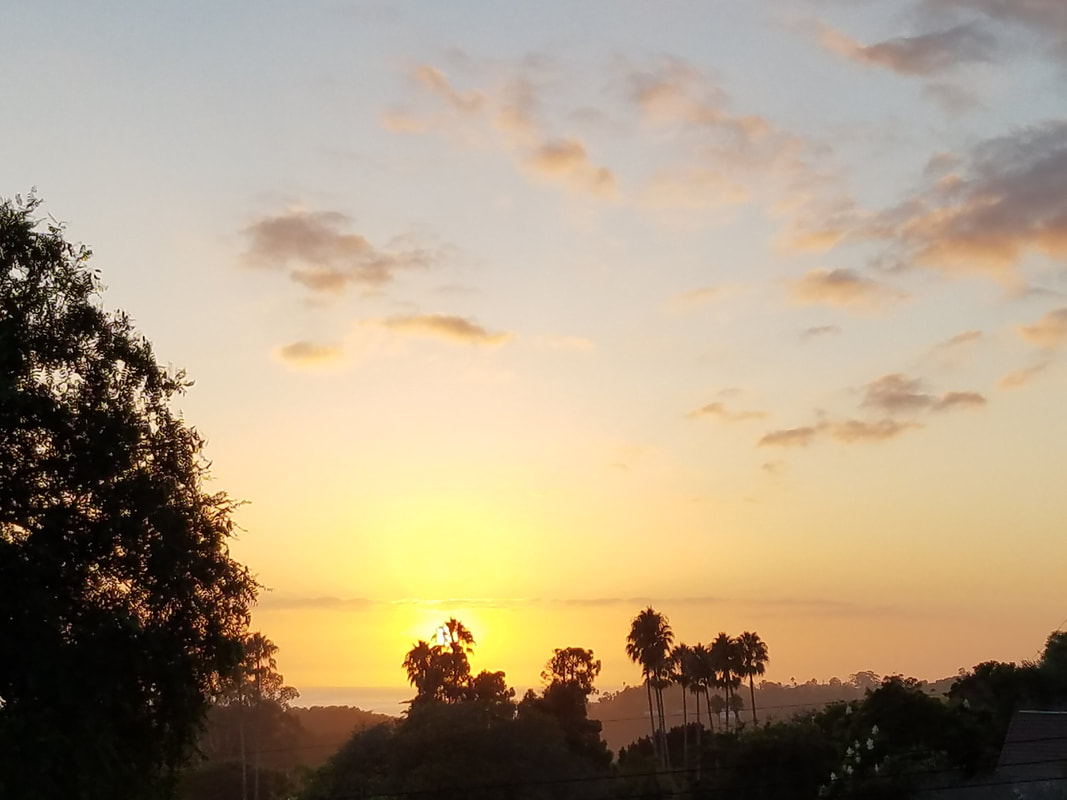
To see a color the wavelength must be in the light source. When you see color, you are seeing wavelengths reflected back to you, the rest of the colors are being absorbed by the surface. Why isn't brown in the spectrum? Because brown is the combination of many colors both in light and paint. How we measure color in light? A part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum called Visible Light is measured in nanometers, nm. This information is useful when understanding the color rendering ability and color bias of various light sources when compared to daylight. The primary colors in light; red + blue-violet + green combine to make white light. The shadows in pure color light make the complimentary colors, found opposite on the color wheel, magenta, turquoise, yellow. Sunset colors are particles in the atmosphere capturing and reflecting light.
To understand why this is so, one need only recall how typical sky colors are produced. The familiar blue of the daytime sky is the result of the selective scattering of sunlight by air molecules. Scattering is the scientific term used to describe the reflection or re-direction of light by small particles .... At sunrise or sunset, sunlight takes a much longer path through the atmosphere than during the middle part of the day. Because this lengthened path results in an increased amount of violet and blue light being scattered out of the beam by the nearly infinite number of scattering "events" that occur along the way (a process collectively known as multiple scattering), the light that reaches an observer early or late in the day is noticeably reddened. Thus, it could be said that sunsets are red because the daytime sky is blue. [1]
|
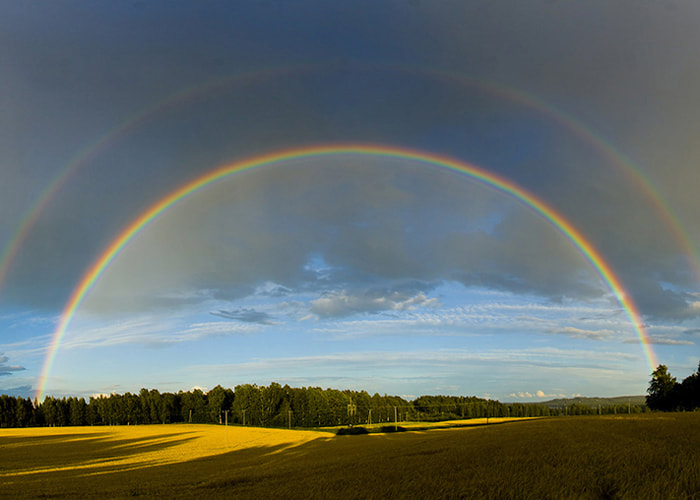
RainbowsIf you are looking for a rainbow, turn your back to the sun at the end of a rainstorm. Particles in the sky, droplets of moisture, split the sunlight in the same way a prism will, creating distinct bands of color. Each water droplet acts like a tiny prism. Light is refracted upon entering the droplet, then reflected onto the back of the droplet, then refracted a second time upon exiting the droplet.
A double rainbow forms when light is reflected twice on the inside of the droplet. Color Vision in Insects and animals
Animals have vision that differs from humans, bees and butterflies see colors we cannot see, more Ultra Violet wavelengths, guiding them to the patterns in flowers. Dogs and cats mostly see."... greys and some blues and yellows." [3]
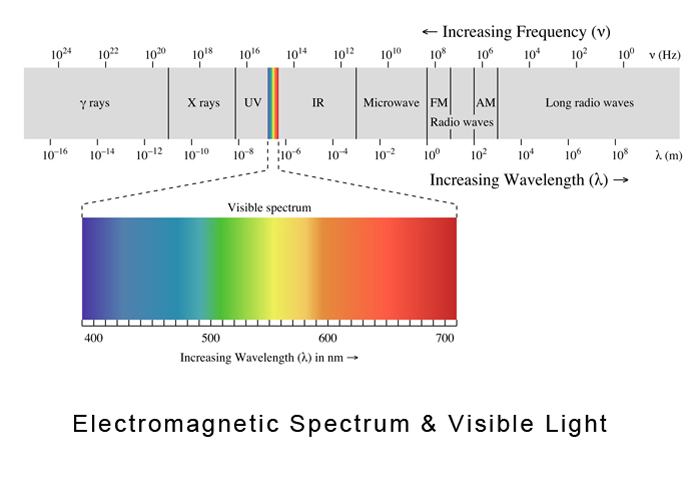
"... In general, humans can see wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum from 400 to 800 nanometers - from violet to red. Insects, on the other hand, perceive wavelengths of from 650 to 300 nanometers, including the ultraviolet range of the spectrum. " [4] Circadian Animals Color in LightElectromagnetic Spectrum & Visible LightVisible light is only part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum surrounding us, X rays;, Ultra Violet Light, UV, Visible Light, Infa Red Light, Microwaves, Radio Waves, and Long waves.
Visible Spectrum
390 to 700 Nanometers, nm, describes the wavelengths visible to the human eye.
Footnotes
Photo Credits
|
- Home
-
- CHROMA Topics
- Color Spectrum - Light is Energy
- Color in Light
- Color in Nature
- Color in Paint
- Why does paint fade?
- Color Names & Meanings
- Color Phenomena
- Color Perception is Individual
- Color In Fashion
- Color for your home
- Color in Space
- Color Blindness
- Color Blind Interview
- Synesthesia
- Synesthete Deborah Borrowdale-Cox
- Synesthete Stephen Orr, BH&G Editor
-
- Circadian & THERAPY Topics
- Circadian Explained
- Circadian Ganglion Cells
- Circadian Melatonin
- Circadian Animals
- Circadian Research
- Autism & Lighting for the Spectrum
- Blue Light Dimming Apps
- Red Night Lights
- Vitamin D & Light
- SAD - Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimers and Light Therapy
- Photosensitivity - Light Sensitive Drugs
- Red Light Therapy
- Sleep & Lighting
- Dreams and Second Sleep
- NASA - Lighting in Space & Undersea
- Jet Lag
- Sunglasses
- Chakras
- Crystals, Minerals, & Gemstones
-
- LIGHTing Design Topics
- UV Germicidal Disinfection Light
- LED Lighting Facts Card
- CRI - Color Rendering Index
- LED TM-30
- LED Kelvin Color
- LED LPW
- LED Flicker
- LED Glare
- OLED - Organic LED
- Human Centric Lighting
- Lighting with Daylighting
- Lighting for Healthy Buildings & Zero Net Energy
- Lighting for Healthcare
- Lighting for Horticulture
- Lighting for Hospitality & LED Retrofits
- Lighting for Museums
- Lighting for Seniors & Low Vision
- Lighting Design Tips & Codes
- Parking Lot Lighting
- Solar Lighting for Humanity & World Health
- Davis Insectary Garden
- Santa Barbara Mesa Insectary Garden
- Home
-
- CHROMA Topics
- Color Spectrum - Light is Energy
- Color in Light
- Color in Nature
- Color in Paint
- Why does paint fade?
- Color Names & Meanings
- Color Phenomena
- Color Perception is Individual
- Color In Fashion
- Color for your home
- Color in Space
- Color Blindness
- Color Blind Interview
- Synesthesia
- Synesthete Deborah Borrowdale-Cox
- Synesthete Stephen Orr, BH&G Editor
-
- Circadian & THERAPY Topics
- Circadian Explained
- Circadian Ganglion Cells
- Circadian Melatonin
- Circadian Animals
- Circadian Research
- Autism & Lighting for the Spectrum
- Blue Light Dimming Apps
- Red Night Lights
- Vitamin D & Light
- SAD - Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimers and Light Therapy
- Photosensitivity - Light Sensitive Drugs
- Red Light Therapy
- Sleep & Lighting
- Dreams and Second Sleep
- NASA - Lighting in Space & Undersea
- Jet Lag
- Sunglasses
- Chakras
- Crystals, Minerals, & Gemstones
-
- LIGHTing Design Topics
- UV Germicidal Disinfection Light
- LED Lighting Facts Card
- CRI - Color Rendering Index
- LED TM-30
- LED Kelvin Color
- LED LPW
- LED Flicker
- LED Glare
- OLED - Organic LED
- Human Centric Lighting
- Lighting with Daylighting
- Lighting for Healthy Buildings & Zero Net Energy
- Lighting for Healthcare
- Lighting for Horticulture
- Lighting for Hospitality & LED Retrofits
- Lighting for Museums
- Lighting for Seniors & Low Vision
- Lighting Design Tips & Codes
- Parking Lot Lighting
- Solar Lighting for Humanity & World Health
- Davis Insectary Garden
- Santa Barbara Mesa Insectary Garden