Circadian Melatonin - Learning Objectives
The sun plays an important role in our wake and sleep cycles, known as your Circadian Rhythm.
Our ancestors evolved under the natural cycles of day-light and dark -night. Light is energy that influences mind and body - many chemicals in our bodies are controlled by light.
MelatoninMelatonin is produced at night to direct our bodies to sleep. Exposure to blue tinted light can delay sleep for as much as two hours.
“Most of the effects of a light exposure comes within the first few minutes.” Shadab Rahman - Meeting the Moment: Lighting and Wellness, IES Webinar 06-03-21
https://sleep.hms.harvard.edu/faculty-staff/shadab-rahman Characterizing the temporal Dynamics of Melatonin and Cortisol Changes in Response to Nocturnal Light Exposure. Authors: Authors: Rahman SA, Wright KP, Lockley SW, Czeisler CA, Gronfier C. Sci Rep 2019-12-23 View full abstract on Pubmed https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31873098/ Twenty-one young healthy participants were randomized to receive either intermittent bright (~9,500 lux) light (IBL), continuous bright light (CBL) or continuous dim (~1 lux) light (VDL) for 6.5 h during the biological night (n = 7 per condition). Melatonin suppression occurred rapidly within the first 5 min and continued until the end of each IBL stimuli (t1/2 = ~13 min). Melatonin recovery occurred more slowly between IBL stimuli (half-maximal recovery rate of ~46 min). Mean melatonin suppression (~40%) and recovery (~50%) were similar across IBL stimuli. [1] Melatonin levels. The change in season can disrupt the balance of the body's level of melatonin, which plays a role in sleep patterns and mood." [2]
SerotoninSerotonin levels. A drop in serotonin, a brain chemical (neurotransmitter) that affects mood, might play a role in SAD. Reduced sunlight can cause a drop in serotonin that may trigger depression. SAD
Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction [3]
Circadian System
Photo receptors in your eyes include Rods, Cones, and Ganglion Cells. Photobiologists and Circadian System Researchers explain how light affects human biology and trends in Circadian Adjusted lighting.
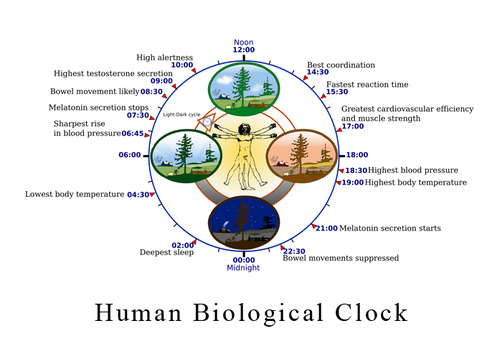
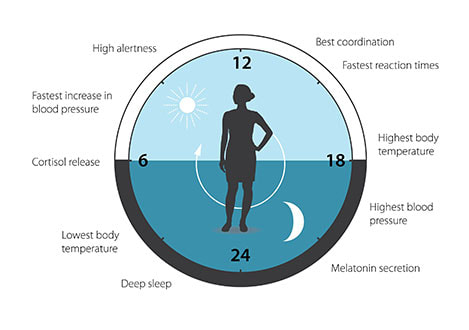
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrKkzm2HQAo This Biological Clock diagram represents the natural circadian rhythm of a human day and night.
"A circadian rhythm /sɜːrˈkeɪdiən/ is any biological process that displays an endogenous, entrainable oscillation of about 24 hours. These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in plants, animals, fungi, and cyanobacteria." [4]
Animals & Plants Circadian Clocks
Animals and plants also have natural Circadian clocks regulating growth and biological processes.
Animals exposed to light pollution will delay their foraging and hunting for several hours after dark, and wait until they have extreme hunger, to begin searching for food. This disruption in their natural cycles creates an imbalance in their biological systems. One study showed that fish would not swim under a bridge brightly lit with blue lighting at night. Many animals grow warmer coats in winter, their fur coats stimulated to grow by the shorter daylight hours with the coming of winter, not the chilling temperatures. While certain ecological problems associated with artificial night lighting are widely known-for instance, the disorientation of sea turtle hatchlings by beachfront lighting-the vast range of influences on all types of animals and plants is only beginning to be recognized. From nest choice and breeding success of birds to behavioral and physiological changes in salamanders, many organisms are seriously affected by human alterations in natural patterns of light and dark. Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting is the first book to consider the environmental effects of the intentional illumination of the night. It brings together leading scientists from around the world to review the state of knowledge on the subject and to describe specific effects that have been observed across a full range of taxonomic groups, including mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians, fishes, invertebrates, and plants. For more information read the book Ecological Consequences of Artificial Night Lighting By Catherine Rich and Travis Longcore. [5] 2017 Nobel Prize for Circadian Rhythm Research
The circadian clock anticipates and adapts our physiology to the different phases of the day. Our biological clock helps to regulate sleep patterns, feeding behavior, hormone release, blood pressure, and body temperature. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017, for their discoveries of molecular mechanisms controlling the circadian rhythm Jeffrey C. Hall, Michael Rosbash, Michael W. Young [6] |
Circadian BrainBrain Signals
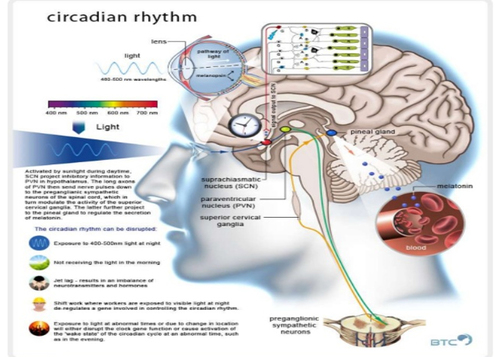
The controller of our Circadian System producing Melatonin is the Pineal Gland, this part of the Endocrine System, sometimes referred to as the 'third eye' is located deep inside our brain, directly above the optic chiasm. . It receives signals though our eyes, collecting information about light intensity and color via the optic nerves. "Suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), located in the hypothalamus above the optic chiasm."
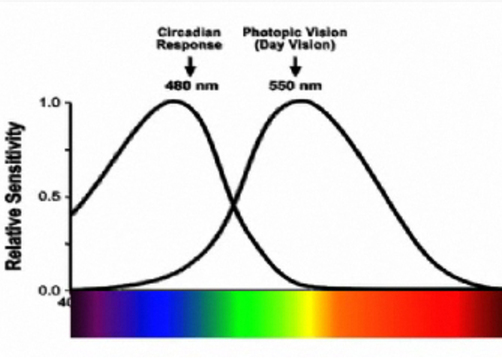
Hormones - Melatonin and Serotonin, are created in our bodies to signal us to sleep and wake. Cyto-architecture is a biology term used to describe the study of the arrangement of cells and how this affects the performance of each organ. Often referred to as study of the brain structure, 'cyto' means 'cells' and 'architecture' originates from Greek arkhitekton 'master builder.' Studying the architecture of the brain, is analogous to the study of buildings, their manner of construction and the arrangement of their parts. As recently as 2002 scientists discovered photoreceptors called ganglion cells (RGC) in our eye's retina that respond to light and send signals to our circadian system. Scientists continue to search for understanding of the brain circuits, receptors, and their functions. [7] Circadian Response Curve
|
- Home
-
- CHROMA Topics
- Color Spectrum - Light is Energy
- Color in Light
- Color in Nature
- Color in Paint
- Why does paint fade?
- Color Names & Meanings
- Color Phenomena
- Color Perception is Individual
- Color In Fashion
- Color for your home
- Color in Space
- Color Blindness
- Color Blind Interview
- Synesthesia
- Synesthete Deborah Borrowdale-Cox
- Synesthete Stephen Orr, BH&G Editor
-
- Circadian & THERAPY Topics
- Circadian Explained
- Circadian Ganglion Cells
- Circadian Melatonin
- Circadian Animals
- Circadian Research
- Autism & Lighting for the Spectrum
- Blue Light Dimming Apps
- Red Night Lights
- Vitamin D & Light
- SAD - Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimers and Light Therapy
- Photosensitivity - Light Sensitive Drugs
- Red Light Therapy
- Sleep & Lighting
- Dreams and Second Sleep
- NASA - Lighting in Space & Undersea
- Jet Lag
- Sunglasses
- Chakras
- Crystals, Minerals, & Gemstones
-
- LIGHTing Design Topics
- UV Germicidal Disinfection Light
- LED Lighting Facts Card
- CRI - Color Rendering Index
- LED TM-30
- LED Kelvin Color
- LED LPW
- LED Flicker
- LED Glare
- OLED - Organic LED
- Human Centric Lighting
- Lighting with Daylighting
- Lighting for Healthy Buildings & Zero Net Energy
- Lighting for Healthcare
- Lighting for Horticulture
- Lighting for Hospitality & LED Retrofits
- Lighting for Museums
- Lighting for Seniors & Low Vision
- Lighting Design Tips & Codes
- Parking Lot Lighting
- Solar Lighting for Humanity & World Health
- Davis Insectary Garden
- Santa Barbara Mesa Insectary Garden
- Home
-
- CHROMA Topics
- Color Spectrum - Light is Energy
- Color in Light
- Color in Nature
- Color in Paint
- Why does paint fade?
- Color Names & Meanings
- Color Phenomena
- Color Perception is Individual
- Color In Fashion
- Color for your home
- Color in Space
- Color Blindness
- Color Blind Interview
- Synesthesia
- Synesthete Deborah Borrowdale-Cox
- Synesthete Stephen Orr, BH&G Editor
-
- Circadian & THERAPY Topics
- Circadian Explained
- Circadian Ganglion Cells
- Circadian Melatonin
- Circadian Animals
- Circadian Research
- Autism & Lighting for the Spectrum
- Blue Light Dimming Apps
- Red Night Lights
- Vitamin D & Light
- SAD - Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimers and Light Therapy
- Photosensitivity - Light Sensitive Drugs
- Red Light Therapy
- Sleep & Lighting
- Dreams and Second Sleep
- NASA - Lighting in Space & Undersea
- Jet Lag
- Sunglasses
- Chakras
- Crystals, Minerals, & Gemstones
-
- LIGHTing Design Topics
- UV Germicidal Disinfection Light
- LED Lighting Facts Card
- CRI - Color Rendering Index
- LED TM-30
- LED Kelvin Color
- LED LPW
- LED Flicker
- LED Glare
- OLED - Organic LED
- Human Centric Lighting
- Lighting with Daylighting
- Lighting for Healthy Buildings & Zero Net Energy
- Lighting for Healthcare
- Lighting for Horticulture
- Lighting for Hospitality & LED Retrofits
- Lighting for Museums
- Lighting for Seniors & Low Vision
- Lighting Design Tips & Codes
- Parking Lot Lighting
- Solar Lighting for Humanity & World Health
- Davis Insectary Garden
- Santa Barbara Mesa Insectary Garden