Synesthesia
See color as music, taste salt and see color; the ability to perceive through your senses information you receive intellectually.
Learning Objectives - Synesthesia
What is Synesthesia ?
Synesthesia is the ability to perceive through your senses information you receive intellectually. This can be experienced as associations of multiple senses, when the stimulation of one sensory system leads to an experience in another system. Why do we separate each sense; taste, smell, sight, sound, and touch? Yes, it is possible to have a blending of our senses in our experience the world.
Synesthesia is a neurological condition in which two or more senses experienced separately are involuntarily joined together. For instance, some synesthetes experience color when they hear sounds or read words. Others experience tastes, smells or shapes. Statistics vary between one in 23 people have Synesthesia [1] and ten people in a million have Synesthesia. Females outnumber males 6 to 1.... There is a strong link between Synesthesia and Photographic Memory. Many Synesthetes used their Synesthesia as a mnemonic aid. [2] Synesthesia examples include; Seeing music as colors. Taste salt and see colors. Days of the week or months appear as colors. Numbers have shapes or colors. Feeling flavors as shapes. Cross-modal association is the comparison of one sense to another. The word synesthesia comes from two Greek words, syn (together) and aisthesis (perception or sensation). Therefore, synesthesia literally means 'joined perception.' When one sensation leads to an experience of a second perception. Cyto-architecture is a biology term used to describe the study of the arrangement of cells and how this affects the performance of each organ. Often referred to as study of the brain structure, 'cyto' means 'cells' and 'architecture' originates from Greek arkhitekton 'master builder.' Studying the architecture of the brain, is analogous to the study of buildings, their manner of construction and the arrangement of their parts. As recently as 2002 scientists discovered photoreceptors called ganglion cells (RGC) in our eye's retina that respond to light and send signals to our circadian system. Scientists continue to search for understanding of the brain circuits, receptors, and their functions. [3] Synesthesia is part of the science of light and sight and this is why it is included here in ChromaTherapyLight. "The colours my daughter 'sees' for each musical note."
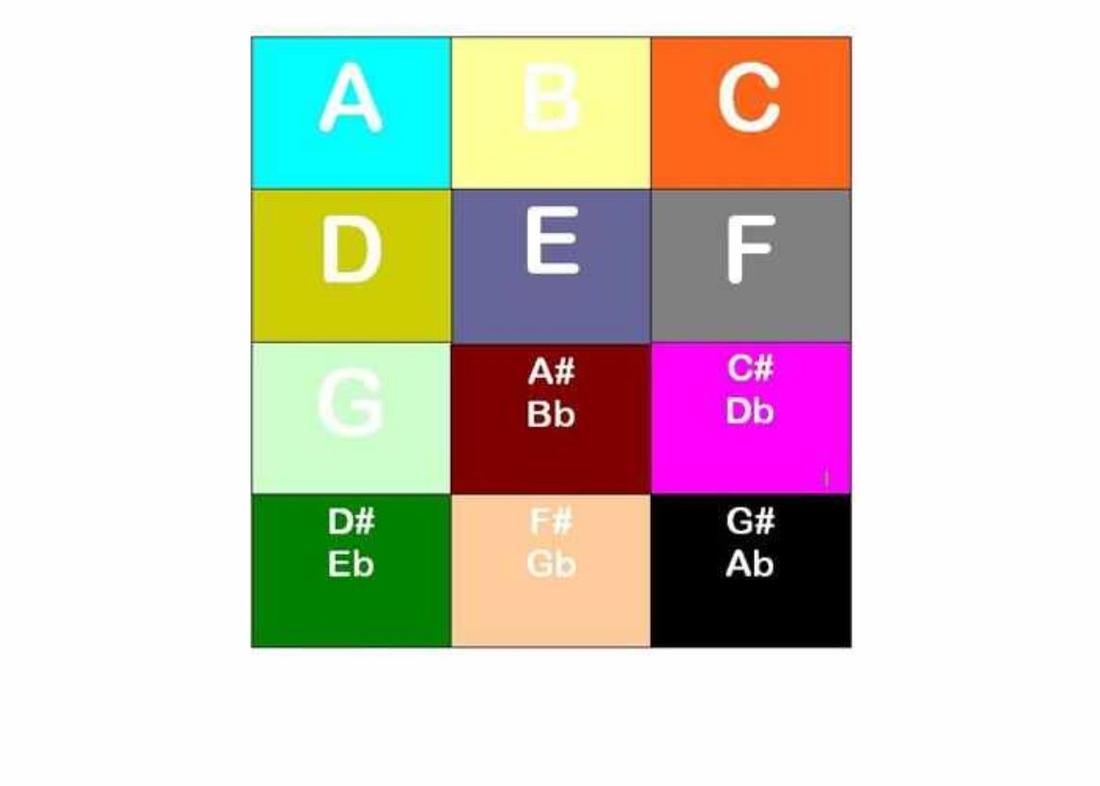
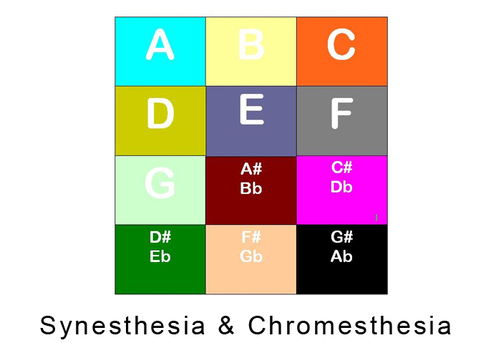
Image by Jess, Photo by Andrew Bullock, 2009 [4] Chromesthesia is also termed sound-color synesthesia. Criteria for Synesthesia [5]
Testing for Synesthesia
What is the Synesthesia Battery?
This battery of tests provides a standard battery of questions, tests and scoring. This test is available to the whole community of researchers and synesthetes for their use in making scientific progress. Your data will be kept entirely private, for use only by yourself, and by a researcher if you provide a valid email address for one. http://www.synesthete.org/ Dr Joel Salinas Synesthesia Test
The University of Sussex Synesthesia Questionnaire is a more general research questionnaire about synesthesia as a whole without placing emphasis on any one specific subtype of synesthesia. If you do have synesthesia, the results from this study can also be used as a way for scientists to find volunteers for future synesthesia-related brain research. https://joelsalinasmd.com/test/ Mirror Touch : A Memoir of Synesthesia and the Secret Life of the BrainDr. Joel Salinas is a Harvard brain doctor with extraordinary gifts that provide him unique access to his patients and enable him to experience life in a remarkable way. He has mirror-touch synesthesia, a neurological trait that allows him to feel others’ emotions and physical sensations. Susceptible to the pain and discomfort of his patients—Salinas uses his heightened empathic ability—what he calls “compulsory mindfulness”—to help understand and better treat their conditions. Using his own experiences as a brain doctor and synesthete, Salinas also shares the remarkable stories of equally remarkable people who similarly live in a heightened state of awareness, whether because of ecstatic seizures from epilepsy, a congenital condition like autism, or after a seemingly debilitating stroke. Written with intelligence and compassion, and anchored by the latest of what we know and what we have yet to decipher in neurology, psychology, psychiatry, and the neurosciences, Mirror Touch is an enthralling investigation into the power of the brain—one that proves that the mind, in wondrous and mysterious fashion, continues to promise exciting and inexhaustible ways to think, to see, and to be.
|
Jason Padgett - Acquired Synesthesia and Savant SyndromeStuck by Genius: How a Brain Injury Made Me a Mathematical Marvel [book] by Jason Padgett and Maureen Ann Seaberg.
In this book, Jason Padgett discusses his recovery from head injury and recognizing his newly acquired math observations and insight about Pi, Fractals, and Fibonacci, termed Mathematical Synesthesia Philippa Stanton
|
Related Topics
|