Color Spectrum - Light is EnergyLight is Energy - Learning Objectives
Color in Light
How we measure color in light? A part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum called Visible Light is measured in nanometers, nm. This information is useful when understanding the color rendering ability and color bias of various light sources when compared to daylight.
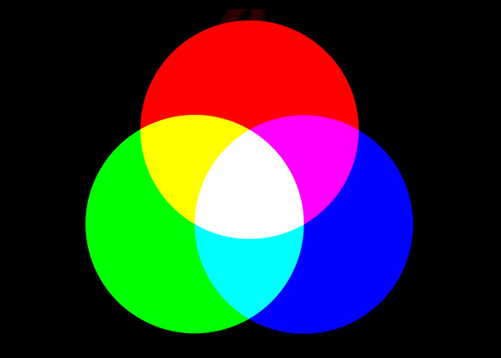
The primary colors in light; red + blue-violet + green combine to make white light as shown in the illustration below. Tri colors forming white light.
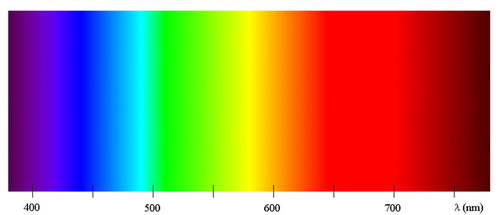
Visible Spectrum390 to 700 Nanometers (nm), describes the wavelengths visible to the human eye. The wavelengths in visible light are measured in Nanometers, corresponding to different colors, shorter wavelengths are seen as blues and blue violet and the longest wavelengths are seen as yellows and reds as illustrated in the rainbow diagram below. A wavelength is the distance measured between successive crests of a wave.
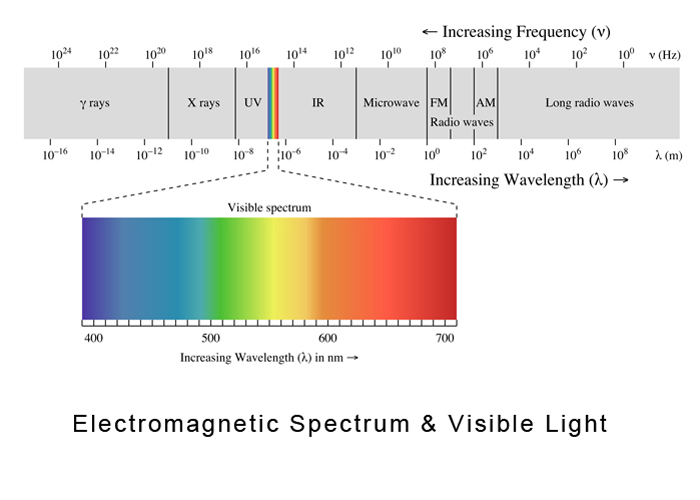
Electromagnetic Spectrum & Visible LightVisible light is only part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum surrounding us, X rays;, Ultra Violet Light, UV, Visible Light, Infa Red Light, Microwaves, Radio Waves, and Long waves.
Colors We Can't See
There are many wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum the human eye cannot detect. Energy with wavelengths too short for humans to see Energy with wavelengths too short to see is "more violet than violet". Light with such short wavelengths is called "Ultraviolet" light. The term "ultra-" means higher than. How do we know this light exists? One way is that this kind of light causes sunburns. Our skin is sensitive to this kind of light. If we stay out in this light without sunblock protection, our skin absorbs this energy. After the energy is absorbed, it can make our skin change color ("tan") or it can break down the cells and cause other damage. Energy with wavelengths too long for humans to see Energy whose wavelength is too long to see is "redder than red". Light with such long wavelengths is called "Infrared" light. The term "Infra-" means "lower than". How do we know this kind of light exists? One way is that we can feel energy with these wavelengths such as when we sit in front of a campfire or when we get close to a stove burner. Scientists like Samuel Pierpont Langley passed light through a prism and discovered that the infrared light the scientists could not see beyond red could make other things hot. Very long wavelengths of infrared light radiate heat to outer space. This radiation is important to the Earth's energy budget. If this energy did not escape to space, the solar energy that the Earth absorbs would continue to heat the Earth. [1] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
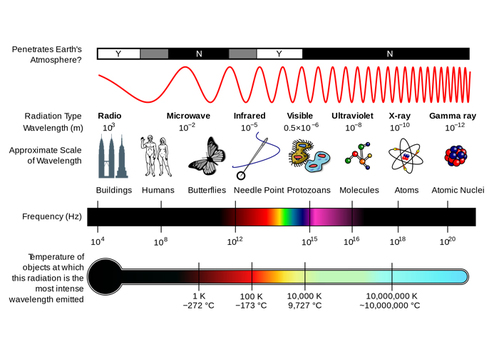
A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths.
Electromagnetic Radiation Spectrum Poster - Click on image to enlarge.
This poster includes all known ranges of EMR including gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared, microwaves, radio waves (ULF, VLF, LF, MF, HF, long, short, HAM, VHF, UHF, SHF, EHF), cosmic microwave background radiation and brain waves, all organized by octaves. The audio frequency spectrum is also included. Descriptions are included for all ranges and properties of EMR including reflection, refraction, LASER, television, gravity waves, emission and absorption. There is also a handy chart of SI unit prefixes ranging from yocto to yotta.
FootnotesPhoto Credits
|
- Home
-
- CHROMA Topics
- Color Spectrum - Light is Energy
- Color in Light
- Color in Nature
- Color in Paint
- Why does paint fade?
- Color Names & Meanings
- Color Phenomena
- Color Perception is Individual
- Color In Fashion
- Color for your home
- Color in Space
- Color Blindness
- Color Blind Interview
- Synesthesia
- Synesthete Deborah Borrowdale-Cox
- Synesthete Stephen Orr, BH&G Editor
-
- Circadian & THERAPY Topics
- Circadian Explained
- Circadian Ganglion Cells
- Circadian Melatonin
- Circadian Animals
- Circadian Research
- Autism & Lighting for the Spectrum
- Blue Light Dimming Apps
- Red Night Lights
- Vitamin D & Light
- SAD - Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimers and Light Therapy
- Photosensitivity - Light Sensitive Drugs
- Red Light Therapy
- Sleep & Lighting
- Dreams and Second Sleep
- NASA - Lighting in Space & Undersea
- Jet Lag
- Sunglasses
- Chakras
- Crystals, Minerals, & Gemstones
-
- LIGHTing Design Topics
- UV Germicidal Disinfection Light
- LED Lighting Facts Card
- CRI - Color Rendering Index
- LED TM-30
- LED Kelvin Color
- LED LPW
- LED Flicker
- LED Glare
- OLED - Organic LED
- Human Centric Lighting
- Lighting with Daylighting
- Lighting for Healthy Buildings & Zero Net Energy
- Lighting for Healthcare
- Lighting for Horticulture
- Lighting for Hospitality & LED Retrofits
- Lighting for Museums
- Lighting for Seniors & Low Vision
- Lighting Design Tips & Codes
- Parking Lot Lighting
- Solar Lighting for Humanity & World Health
- Davis Insectary Garden
- Santa Barbara Mesa Insectary Garden
- Home
-
- CHROMA Topics
- Color Spectrum - Light is Energy
- Color in Light
- Color in Nature
- Color in Paint
- Why does paint fade?
- Color Names & Meanings
- Color Phenomena
- Color Perception is Individual
- Color In Fashion
- Color for your home
- Color in Space
- Color Blindness
- Color Blind Interview
- Synesthesia
- Synesthete Deborah Borrowdale-Cox
- Synesthete Stephen Orr, BH&G Editor
-
- Circadian & THERAPY Topics
- Circadian Explained
- Circadian Ganglion Cells
- Circadian Melatonin
- Circadian Animals
- Circadian Research
- Autism & Lighting for the Spectrum
- Blue Light Dimming Apps
- Red Night Lights
- Vitamin D & Light
- SAD - Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimers and Light Therapy
- Photosensitivity - Light Sensitive Drugs
- Red Light Therapy
- Sleep & Lighting
- Dreams and Second Sleep
- NASA - Lighting in Space & Undersea
- Jet Lag
- Sunglasses
- Chakras
- Crystals, Minerals, & Gemstones
-
- LIGHTing Design Topics
- UV Germicidal Disinfection Light
- LED Lighting Facts Card
- CRI - Color Rendering Index
- LED TM-30
- LED Kelvin Color
- LED LPW
- LED Flicker
- LED Glare
- OLED - Organic LED
- Human Centric Lighting
- Lighting with Daylighting
- Lighting for Healthy Buildings & Zero Net Energy
- Lighting for Healthcare
- Lighting for Horticulture
- Lighting for Hospitality & LED Retrofits
- Lighting for Museums
- Lighting for Seniors & Low Vision
- Lighting Design Tips & Codes
- Parking Lot Lighting
- Solar Lighting for Humanity & World Health
- Davis Insectary Garden
- Santa Barbara Mesa Insectary Garden